The Covid-19 Pandemic led to accelerated uptake of different digital technologies in a way that was unforeseen. Some estimates say that the world has taken a 10-year leap in terms of digital technology adoption. Today we have seamless cloud meetings, online learning, several health monitoring tools, booming e-commerce, automated manufacturing, better supply chain systems and many more.
Some of the technologies already existed, while others are recent innovations by people responding to the pandemic. Many of these have now gained widespread acceptance. How did this happen?
The disruption caused by Covid-19 led to a turning point that promoted the adoption of new technologies. Usually, new technologies go through an adoption lifecycle that starts with innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggards. With a disruptive event, the time it takes for the early and late majority to onboard is short, hence a technology can gain massive acceptance within a very short time.
Background
The timing of the Covid-19 pandemic presented an opportune time for use of digital technologies. The world had become more connected with affordable broadband internet connection is available in many places. The availability of smartphones also made it easy to use digital technologies even in areas where computers are not available.
With this background, digital technologies could thrive. Developers went for digital tools to respond to various challenges such as contact tracing. The government needed ways to keep track of vaccine distribution. Shops needed to keep selling even when communities were in lockdown. Schools needed to keep teaching even when physical school attendance was limited. Solutions lay in digital technologies.
The nature of the pandemic also helped to encourage digital interventions. Covid-19 is spread majorly by close contact to an infected person. This called for limiting physical interactions and public gathering – the very things that are crucial for human existence. To compensate for these, digital technologies could be used to connect people where physical meetings were not possible. E-commerce was necessary if people were not to go to malls as before. Many technologies to make this possible existed, but had not received widespread adoption.
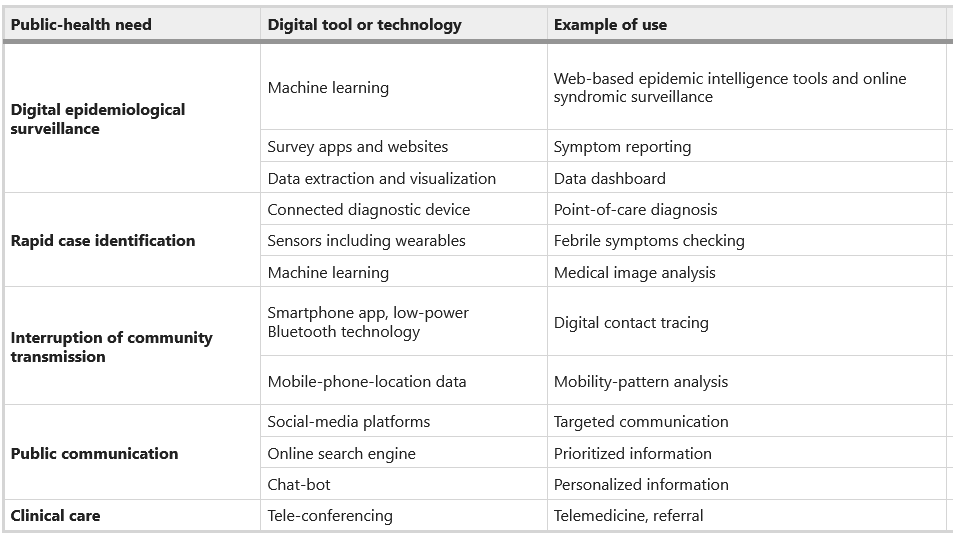
Digital technologies are also at the center of public health responses needed to fight Covid-19. The table below shows examples of digital technologies in public health intervention.
Covid-19 Responses in Kenya
In Kenya, the government implemented several responses to slow down the spread of Covid-19. Some of these include:
- Requiring physical distancing in all places.
- Enforcement of dawn to dusk curfew.
- Restriction of movement from some geographical locations.
- Closure of schools.
- Requirement for people not providing essential services to work from home.
- Ban on mass gatherings.
- Active disease surveillance.
- Economic stimulus packages to employers and employees.
- Encouraging the use of non-cash transactions.
Many of these responses involved the use of digital technologies to implement, or to help cope with the new normal.
Adoption of Digital Technologies
With the closure of schools, learning was supposed to take place remotely, something that had barely been happening before (except in some Universities). This meant that teachers and students needed to get creative and find out what could work in their context. They used cloud meeting platforms to conduct classes where the Internet was available and students could afford the necessary devices. Teachers had to learn how to use the different platforms and many acquired crucial digital skills. In some cases, they had to improvise and use platforms such as WhatsApp.
This exposure to digital technologies is very useful in the sense that it makes them open to adopting other digital technologies. Running a successful online class gives the teacher the confidence to adopt other technologies, and even continue using the same after the pandemic.
With reduced income and job losses, many people tried their hand in business. This led to many people setting up their own websites and online shops to allow buyers to access their products online. Faced with a different operating environment, many businesses moved online in 2020. This is another way that people were introduced to digital technologies.
There was also an upsurge in the use of cashless payment solutions. In Kenya, the Central Bank negotiated for reduced tariffs for mobile money services, as well as free movement of money from mobile wallets to the bank and vice versa. This led to an increase in the use of cashless transactions and it become normal for small traders to accept payment via mobile money. This is likely to remain even in the post-pandemic world.
The use of digital technologies to track vaccine rollout in Kenya is also a significant step forward in managing healthcare. This could set the stage for more ehealth functions when people see the need for it. Already, there are businesses that are working to make telemedicine a possibility in Kenya.
Reduced movement of people led to a boom in eCommerce. Some people who had never ordered goods or services online found themselves with little or no option, and many are now open to shopping online and having their goods delivered without having to physically visit the stores.
The need to work remotely forced people to invest in different tools to make this a reality. This led to an increase in internet usage, and people were buying more equipment such as smartphones and computers. Home internet connections increased, and these opened possibilities for the adoption of more digital technologies.
Conclusion
The Covid-19 pandemic may have forced people to result to digital technologies to solve their most pressing needs, but the results will outlast the Covid-19. We will see a world that is more open to digital technologies and also developers focusing on more of these technologies. This is one positive outcome of the pandemic.